LINUX實戰:TensorFlowSharp入門使用C#編寫TensorFlow人工智能應用
《LINUX實戰:TensorFlowSharp入門使用C#編寫TensorFlow人工智能應用》要點:
本文介紹了LINUX實戰:TensorFlowSharp入門使用C#編寫TensorFlow人工智能應用,希望對您有用。如果有疑問,可以聯系我們。
TensorFlowSharp入門使用C#編寫TensorFlow人工智能利用學習.
TensorFlow簡單先容
TensorFlow 是谷歌的第二代機器學習系統,依照谷歌所說,在某些基準測試中,TensorFlow的表現比第一代的DistBelief快了2倍.
TensorFlow 內建深度學習的擴展支持,任何能夠用計算流圖形來表達的計算,都可以使用TensorFlow.任何基于梯度的機器學習算法都能夠受益于TensorFlow的自動分解(auto-differentiation).通過靈活的Python接口,要在TensorFlow中表達想法也會很容易.
TensorFlow 對于實際的產物也是很有意義的.將思路從桌面GPU訓練無縫搬遷到手機中運行.
示例Python代碼:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np # Create 100 phony x, y data points in NumPy, y = x * 0.1 + 0.3 x_data = np.random.rand(100).astype(np.float32) y_data = x_data * 0.1 + 0.3 # Try to find values for W and b that compute y_data = W * x_data + b # (We know that W should be 0.1 and b 0.3, but TensorFlow will # figure that out for us.) W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1], -1.0, 1.0)) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1])) y = W * x_data + b # Minimize the mean squared errors. loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_data)) optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5) train = optimizer.minimize(loss) # Before starting, initialize the variables. We will 'run' this first. init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # Launch the graph. sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) # Fit the line. for step in range(201): sess.run(train) if step % 20 == 0: print(step, sess.run(W), sess.run(b)) # Learns best fit is W: [0.1], b: [0.3]?
使用TensorFlowSharp?
GitHub:https://github.com/migueldeicaza/TensorFlowSharp
官方源碼庫,該項目支持跨平臺,使用Mono.
可以使用NuGet 安裝TensorFlowSharp,如下:
Install-Package TensorFlowSharp
編寫簡單應用
使用VS2017新建一個.NET Framework 節制臺應用 tensorflowdemo,接著添加TensorFlowSharp 引用.
TensorFlowSharp 包比擬大,需要耐心等待.
然后在項目屬性中生成->平臺目的 改為 x64.
打開Program.cs 寫入如下代碼:
運行程序成果如下:
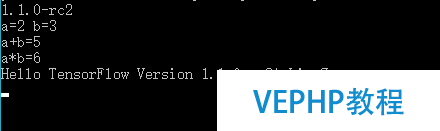
?
TensorFlow C# image recognition
圖像辨認示例體驗
https://github.com/migueldeicaza/TensorFlowSharp/tree/master/Examples/ExampleInceptionInference
下面學習一個實際的人工智能應用,是非常簡單的一個示例,圖像辨認.
新建一個 imagerecognition .NET Framework 節制臺應用項目,接著添加TensorFlowSharp 引用.
然后在項目屬性中生成->平臺目的 改為 x64.
接著編寫如下代碼: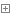
class Program { static string dir, modelFile, labelsFile; public static void Main(string[] args) { dir = "tmp"; List<string> files = Directory.GetFiles("img").ToList(); ModelFiles(dir); var graph = new TFGraph(); // 從文件加載序列化的GraphDef var model = File.ReadAllBytes(modelFile); //導入GraphDef graph.Import(model, ""); using (var session = new TFSession(graph)) { var labels = File.ReadAllLines(labelsFile); Console.WriteLine("TensorFlow圖像識別 LineZero"); foreach (var file in files) { // Run inference on the image files // For multiple images, session.Run() can be called in a loop (and // concurrently). Alternatively, images can be batched since the model // accepts batches of image data as input. var tensor = CreateTensorFromImageFile(file); var runner = session.GetRunner(); runner.AddInput(graph["input"][0], tensor).Fetch(graph["output"][0]); var output = runner.Run(); // output[0].Value() is a vector containing probabilities of // labels for each image in the "batch". The batch size was 1. // Find the most probably label index. var result = output[0]; var rshape = result.Shape; if (result.NumDims != 2 || rshape[0] != 1) { var shape = ""; foreach (var d in rshape) { shape += $"7la94w5njlq9 "; } shape = shape.Trim(); Console.WriteLine($"Error: expected to produce a [1 N] shaped tensor where N is the number of labels, instead it produced one with shape [{shape}]"); Environment.Exit(1); } // You can get the data in two ways, as a multi-dimensional array, or arrays of arrays, // code can be nicer to read with one or the other, pick it based on how you want to process // it bool jagged = true; var bestIdx = 0; float p = 0, best = 0; if (jagged) { var probabilities = ((float[][])result.GetValue(jagged: true))[0]; for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.Length; i++) { if (probabilities[i] > best) { bestIdx = i; best = probabilities[i]; } } } else { var val = (float[,])result.GetValue(jagged: false); // Result is [1,N], flatten array for (int i = 0; i < val.GetLength(1); i++) { if (val[0, i] > best) { bestIdx = i; best = val[0, i]; } } } Console.WriteLine($"{Path.GetFileName(file)} 最佳匹配: [{bestIdx}] {best * 100.0}% 標識為:{labels[bestIdx]}"); } } Console.ReadKey(); } // Convert the image in filename to a Tensor suitable as input to the Inception model. static TFTensor CreateTensorFromImageFile(string file) { var contents = File.ReadAllBytes(file); // DecodeJpeg uses a scalar String-valued tensor as input. var tensor = TFTensor.CreateString(contents); TFGraph graph; TFOutput input, output; // Construct a graph to normalize the image ConstructGraphToNormalizeImage(out graph, out input, out output); // Execute that graph to normalize this one image using (var session = new TFSession(graph)) { var normalized = session.Run( inputs: new[] { input }, inputValues: new[] { tensor }, outputs: new[] { output }); return normalized[0]; } } // The inception model takes as input the image described by a Tensor in a very // specific normalized format (a particular image size, shape of the input tensor, // normalized pixel values etc.). // // This function constructs a graph of TensorFlow operations which takes as // input a JPEG-encoded string and returns a tensor suitable as input to the // inception model. static void ConstructGraphToNormalizeImage(out TFGraph graph, out TFOutput input, out TFOutput output) { // Some constants specific to the pre-trained model at: // https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/models/inception5h.zip // // - The model was trained after with images scaled to 224x224 pixels. // - The colors, represented as R, G, B in 1-byte each were converted to // float using (value - Mean)/Scale. const int W = 224; const int H = 224; const float Mean = 117; const float Scale = 1; graph = new TFGraph(); input = graph.Placeholder(TFDataType.String); output = graph.Div( x: graph.Sub( x: graph.ResizeBilinear( images: graph.ExpandDims( input: graph.Cast( graph.DecodeJpeg(contents: input, channels: 3), DstT: TFDataType.Float), dim: graph.Const(0, "make_batch")), size: graph.Const(new int[] { W, H }, "size")), y: graph.Const(Mean, "mean")), y: graph.Const(Scale, "scale")); } /// <summary> /// 下載初始Graph和標簽 /// </summary> /// <param name="dir"></param> static void ModelFiles(string dir) { string url = "https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/models/inception5h.zip"; modelFile = Path.Combine(dir, "tensorflow_inception_graph.pb"); labelsFile = Path.Combine(dir, "imagenet_comp_graph_label_strings.txt"); var zipfile = Path.Combine(dir, "inception5h.zip"); if (File.Exists(modelFile) && File.Exists(labelsFile)) return; Directory.CreateDirectory(dir); var wc = new WebClient(); wc.DownloadFile(url, zipfile); ZipFile.ExtractToDirectory(zipfile, dir); File.Delete(zipfile); } }
這里必要注意的是由于必要下載初始Graph和標簽,而且是google的站點,所以得使用一些特殊手段.
最終我隨意下載了幾張圖放到bin\Debug\img
?
?然后運行法式,首先確保bin\Debug\tmp文件夾下有tensorflow_inception_graph.pb及imagenet_comp_graph_label_strings.txt.
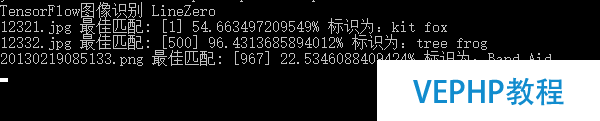
?
人工智能的魅力非常年夜,本文只是一個入門,復制上面的代碼,你沒法訓練模型等等操作.所以道路還是很遠,需一步一步來.
更多可以查看 https://github.com/migueldeicaza/TensorFlowSharp 及?https://github.com/tensorflow/models
本文永遠更新鏈接地址:
學習更多LINUX教程,請查看站內專欄,如果有LINUX疑問,可以加QQ交流《LINUX實戰:TensorFlowSharp入門使用C#編寫TensorFlow人工智能應用》。
轉載請注明本頁網址:
http://www.snjht.com/jiaocheng/9816.html
同類教程排行
- LINUX入門:CentOS 7卡在開機
- LINUX實戰:Ubuntu下muduo
- LINUX教程:Ubuntu 16.04
- LINUX教程:GitBook 使用入門
- LINUX實操:Ubuntu 16.04
- LINUX教學:Shell、Xterm、
- LINUX教程:Linux下開源的DDR
- LINUX實戰:TensorFlowSh
- LINUX教學:Debian 9 'St
- LINUX實戰:Ubuntu下使用Vis
- LINUX教學:Linux 下 Free
- LINUX教學:openslide-py
- LINUX實操:Kali Linux安裝
- LINUX教學:通過PuTTY進行端口映
- LINUX教程:Ubuntu 16.04
